We used NTCIR-10 Japanese-English patent sentence pairs. We used 3,000,000 Japanese-English patent sentence pairs for the training. We used Mecab [8] as the morphological analyzer and the standing tokenizer of Moses [6].
- Making Japanese-English patterns
We used a word dictionary with
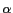 = 0.1 to make the
Japanese-English translation patterns. (
= 0.1 to make the
Japanese-English translation patterns. (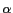 is used in Step 2 of
Section 4.1.) As a result, we obtained 31,843 Japanese-English
word pairs (word dictionary) and 3,158,406 Japanese-English
translation patterns from the training.
is used in Step 2 of
Section 4.1.) As a result, we obtained 31,843 Japanese-English
word pairs (word dictionary) and 3,158,406 Japanese-English
translation patterns from the training.
- Generating Japanese translation sentences
We used a word dictionary with
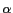 = 0.01 to generate the
Japanese translation sentences. As a result, we obtained 125,194
Japanese-English word pairs (word dictionary).
= 0.01 to generate the
Japanese translation sentences. As a result, we obtained 125,194
Japanese-English word pairs (word dictionary).
We used about 3,000,000 Japanese-English sentence pairs to calculate the English word tri-gram for the language model.
We used Moses [6] as the phrase-based SMT for comparison.
For comparison, we used the art of trial rule-based machine translation system as a rule-base machine translation.