

Next: Power
Up: 3. New Positional Features
Previous: 3. New Positional Features
In Japanese, a mora basically corresponds to a syllable,
the exceptions are prolonged syllables with two moras.
As is well known, a Japanese word of M mora length has
M+1 accent types expressed by mora position of pitch-drop.
Fujisaki et al. proposed a practical f0 estimation method
based on these accent types [5].
Conventional synthesis methods usually estimate f0
contours of target words using some method like this,
and select waveforms with estimated f0 values
or manipulate them to yield the required values.
We use the mora position of the syllable
within the word directly
to represent the pitch of the syllable
because this eliminates the need to consider the f0 value itself.
A careful investigation of the f0 contours
of Japanese city names and town names
clarified that most city and town names with the same mora length
have the same accent type, especially among words with four to six mora.
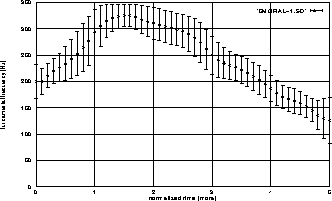
Figure 1 shows the mean f0 contour and standard deviations
obtained from 2,800 of Japanese city and town names with five moras
pronounced by a single narrator.
Standard deviations are small enough to neglect accent types.
Consequently, the f0 of a syllable within
a word of mora length M can be represented
by its mora position m and M.
Figure 1:
Means and standard deviations of f0
 |


Next: Power
Up: 3. New Positional Features
Previous: 3. New Positional Features
Jin'ichi Murakami
2000-01-17
