


�$B The path calculation for
�$B>e$X�(B: RECOGNITION ALGORITHM REDUCING THE
�$BLa$k�(B: RECOGNITION ALGORITHM REDUCING THE
Beam search is employed to decrease the computational cost.
In Viterbi search, at each time t, we compute the
probability of all possible combinations. In comparison with
beam search algorithm, at time t, we only compute the
probability of most likely word combinations within a beam
width 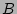 . Assuming a large enough beam, we can be confident
that the globally optimal Viterbi path almost always exists
within that beam. So the beam search algorithm reduces
computation while still providing globally optimal
solutions. In step5 of the algorithm, the best
. Assuming a large enough beam, we can be confident
that the globally optimal Viterbi path almost always exists
within that beam. So the beam search algorithm reduces
computation while still providing globally optimal
solutions. In step5 of the algorithm, the best 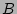 value of
value of
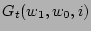 for each frame is calculated. Beam search
has the following advantages.
for each frame is calculated. Beam search
has the following advantages.
- Reduction of Memory and Computational Cost
For Viterbi search,
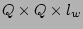 memory cells
are needed to store
memory cells
are needed to store
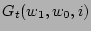 . The beam search, however
only needs
. The beam search, however
only needs  . Therefore, the memory needed to use this
algorithm is significantly reduced. The computational cost
is also reduced by the same ratio.
. Therefore, the memory needed to use this
algorithm is significantly reduced. The computational cost
is also reduced by the same ratio.
- Reduction of the Access Count to Obtain Trigram
Probability
The trigram probabilities when using the beam search are
best stored in a list structure to save memory. Therefore,
to obtain the trigram probabilities, the indices needed to
be calculated. As a result, with beam search, the total
number of indices to obtain trigram probabilities is
reduced. As a result, the computational cost is reduced.



�$B The path calculation for
�$B>e$X�(B: RECOGNITION ALGORITHM REDUCING THE
�$BLa$k�(B: RECOGNITION ALGORITHM REDUCING THE
Jin'ichi Murakami
�$BJ?@.�(B13�$BG/�(B2�$B7n�(B19�$BF|�(B
![]() . Assuming a large enough beam, we can be confident
that the globally optimal Viterbi path almost always exists
within that beam. So the beam search algorithm reduces
computation while still providing globally optimal
solutions. In step5 of the algorithm, the best
. Assuming a large enough beam, we can be confident
that the globally optimal Viterbi path almost always exists
within that beam. So the beam search algorithm reduces
computation while still providing globally optimal
solutions. In step5 of the algorithm, the best ![]() value of
value of
![]() for each frame is calculated. Beam search
has the following advantages.
for each frame is calculated. Beam search
has the following advantages.